Promiscuity Gene DRD4 Test
Discover if your DNA influences your likelihood of infidelity.
Measures:
- Discover your genetic predisposition to infidelity
- Gain insights into your behavioral tendencies
- Discreet and confidential
Collection methods:
Buccal swabs
$149.00
- Discreet shipping
- Accredited lab
- Secure Online Results
- Highest accuracy
- Discreet
- Results in 1-3 business days
About the test
Are You Genetically Predisposed to Promiscuity?
The “promiscuity” gene is a genetic variant of the DRD4 gene, specifically the 7R+ version, which is associated with an increased likelihood of sexual promiscuity.
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter in the brain, plays a key role in feelings of reward and pleasure. The DRD4 gene encodes the dopamine receptor D4, which binds dopamine and transmits the pleasurable signals throughout the body. The 7R+ version of the gene results in altered receptors that bind dopamine less efficiently compared to the more common 4R version, leading to reduced transmission of dopamine signals.
Individuals with the 7R+ variants require higher levels of dopamine to feel the same “good” effects, and sexual activity has been shown to increase dopamine levels, contributing to a greater desire for novelty-seeking behaviors, such as promiscuity. This test helps you understand how this genetic variation may influence your behavioral patterns.
Genetic Profile
How the DRD4 Gene Influences Sexual Behavior
The DRD4 gene, located on chromosome 11, plays a role in regulating dopamine receptors. Inheriting the “promiscuity” variant (7R+) of this gene is linked to a higher likelihood of increased promiscuity and having more extra-pair sexual partners.
The DRD4 gene contains a 48-base pair repeat region where the number of repeats can range from 2 to 11. You inherit two copies of this gene—one from each parent—which means you could inherit two identical copies (e.g., both 4R) or two different ones (e.g., 4R and 7R).
This test identifies the length of the repeat region in each of your DRD4 alleles, revealing how many repeats you have. If you inherit at least one 7R+ allele (7R, 8R, 9R, 10R, or 11R), you’re more likely to exhibit promiscuous behavior compared to individuals with 7R- alleles (fewer than 7 repeats).
The most common variant of the DRD4 gene worldwide is the 4R version, present in approximately 65% of people. The next most common is the 7R version, found in about 20%, followed by the 2R allele (9%). Alleles with eight or more repeats are rare, accounting for less than 1% of the population. The prevalence of the 7R variant differs by region—it’s rare in East and South Asian populations but more common in the Americas.
Understanding the DRD4 Gene and Its Variants
The DRD4 gene contains a 48-base pair repeat region where the number of repeats can range from 2 to 11. You inherit two copies of this gene—one from each parent—which means you could inherit two identical copies (e.g., both 4R) or two different ones (e.g., 4R and 7R).
This test identifies the length of the repeat region in each of your DRD4 alleles, revealing how many repeats you have. If you inherit at least one 7R+ allele (7R, 8R, 9R, 10R, or 11R), you’re more likely to exhibit promiscuous behavior compared to individuals with 7R- alleles (fewer than 7 repeats).
Global Frequency and Other Conditions Linked to the DRD4 Gene
The most common variant of the DRD4 gene worldwide is the 4R version, present in approximately 65% of people. The next most common is the 7R version, found in about 20%, followed by the 2R allele (9%). Alleles with eight or more repeats are rare, accounting for less than 1% of the population. The prevalence of the 7R variant differs by region—it’s rare in East and South Asian populations but more common in the Americas.
How it works


CHOOSE TEST

COLLECT SAMPLE

GET YOUR RESULTS

You might also like
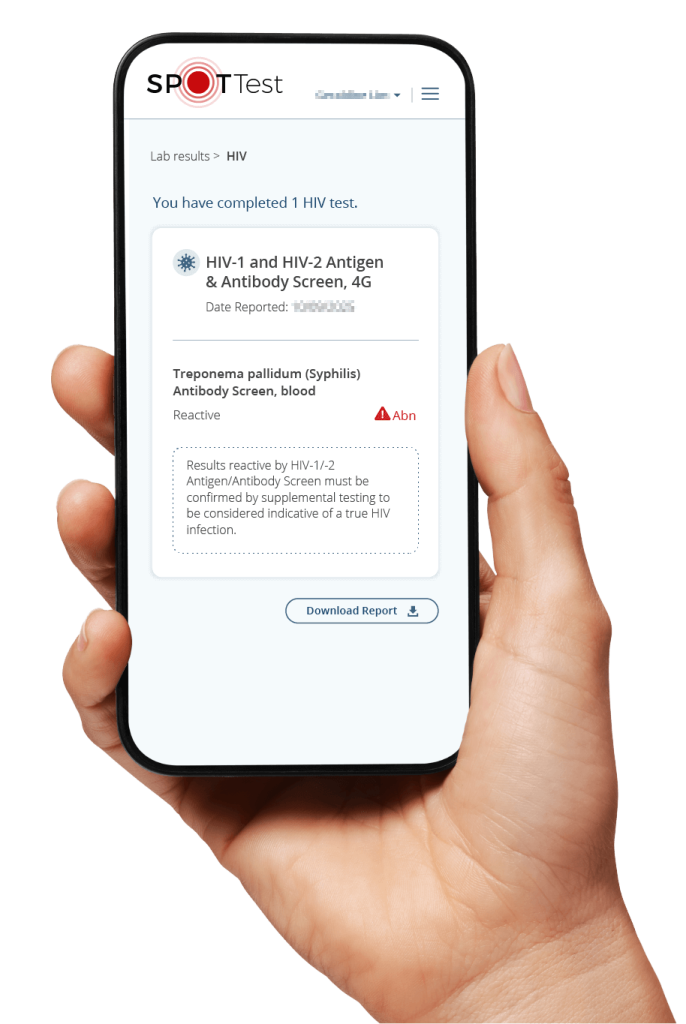
How the DRD4 Gene Influences Sexual Behavior
The DRD4 gene, located on chromosome 11, plays a role in regulating dopamine receptors. Inheriting the “promiscuity” variant (7R+) of this gene is linked to a higher likelihood of increased promiscuity and having more extra-pair sexual partners.