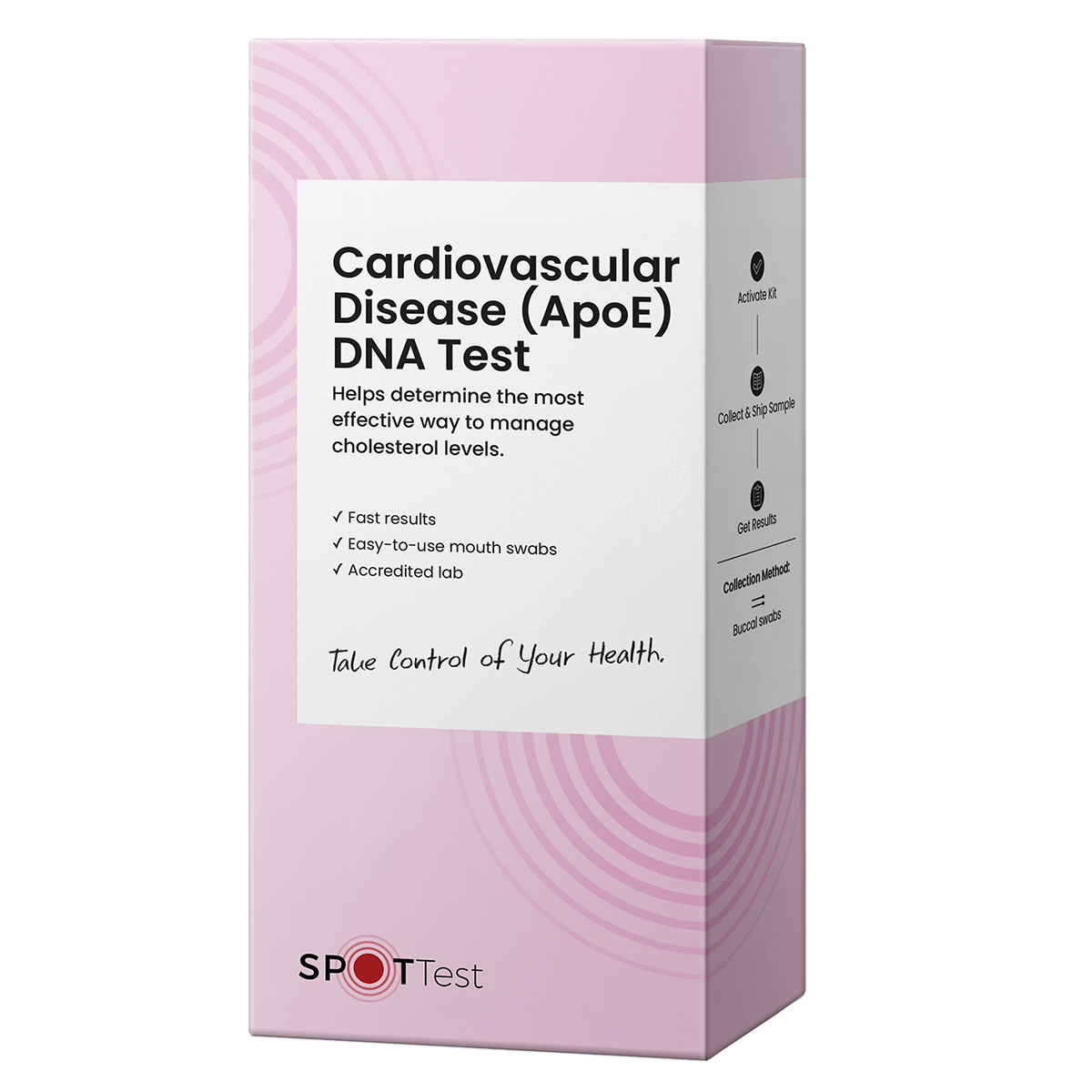
Cardiovascular Disease (ApoE) DNA Test
The APOE gene affects your risk of cardiovascular disease and helps determine the most effective way to manage cholesterol levels.
Measures:
- Analyzes key variants of the APOE gene
- The e2 allele is linked to a higher risk of hyperlipoproteinemia type III
- The e4 allele is associated with elevated LDL cholesterol and increased heart disease risk
- Gain insights into the best strategies for managing your cardiovascular health
Collection methods:
Buccal swabs
$195.00
- Discreet shipping
- Accredited lab
- Secure Online Results
- Highest accuracy
- Discreet
- Results in 1-3 business days
About the test
Understand Your Genetic Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including heart attacks and strokes, is influenced by both lifestyle and genetics. One key factor in heart health is cholesterol balance, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly known as “bad” cholesterol. Elevated LDL levels contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
The APOE gene plays a crucial role in cholesterol metabolism and influences how your body responds to dietary changes and cholesterol-lowering medications. Certain APOE variants are linked to an increased risk of high LDL cholesterol, hyperlipoproteinemia type III, and early-onset cardiovascular disease.
This DNA test analyzes your APOE genotype to help you understand your genetic predisposition to high cholesterol and heart disease. With this knowledge, you can take proactive steps to manage your cardiovascular health effectively.
Genetic Profile
The Role of APOE in Cardiovascular Health
The APOE gene is a key genetic factor in cardiovascular disease risk. It encodes Apolipoprotein E (ApoE), a protein that plays a crucial role in cholesterol transport, metabolism, and clearance, influencing overall heart health.
The APOE gene has different versions, or alleles, that influence cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. The three most common alleles are:
- e3 – The most common, neutral allele with no significant impact on CVD risk.
- e4 – Linked to higher LDL-cholesterol levels and an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
- e2 – Associated with lower LDL-cholesterol but a higher risk of hyperlipoproteinemia type III, which can contribute to CVD.
- e3/e3 or e3/e2 – No increased risk of CVD.
- e2/e2 – Lower LDL-cholesterol but a higher risk of hyperlipoproteinemia type III.
- e3/e4 or e4/e4 – Elevated LDL-cholesterol and increased CVD risk.
- e3/e4 & e4/e4 – A low-fat diet is recommended, as these individuals have difficulty metabolizing fats. They also have a reduced response to statins.
- e2/e2 & e2/e3 – More efficient fat metabolism but reduced carbohydrate metabolism. They tend to respond better to statins.
Understanding your APOE genotype can help tailor diet and medication choices to manage cardiovascular health effectively.
Understanding APOE and Cardiovascular Risk
The APOE gene has different versions, or alleles, that influence cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. The three most common alleles are:
- e3 – The most common, neutral allele with no significant impact on CVD risk.
- e4 – Linked to higher LDL-cholesterol levels and an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
- e2 – Associated with lower LDL-cholesterol but a higher risk of hyperlipoproteinemia type III, which can contribute to CVD.
How Your APOE Genotype Affects Your Risk
- e3/e3 or e3/e2 – No increased risk of CVD.
- e2/e2 – Lower LDL-cholesterol but a higher risk of hyperlipoproteinemia type III.
- e3/e4 or e4/e4 – Elevated LDL-cholesterol and increased CVD risk.
APOE and Lifestyle Response
- e3/e4 & e4/e4 – A low-fat diet is recommended, as these individuals have difficulty metabolizing fats. They also have a reduced response to statins.
- e2/e2 & e2/e3 – More efficient fat metabolism but reduced carbohydrate metabolism. They tend to respond better to statins.
Understanding your APOE genotype can help tailor diet and medication choices to manage cardiovascular health effectively.
How it works


CHOOSE TEST

COLLECT SAMPLE

GET YOUR RESULTS

You might also like
The Role of APOE in Cardiovascular Health
The APOE gene is a key genetic factor in cardiovascular disease risk. It encodes Apolipoprotein E (ApoE), a protein that plays a crucial role in cholesterol transport, metabolism, and clearance, influencing overall heart health.