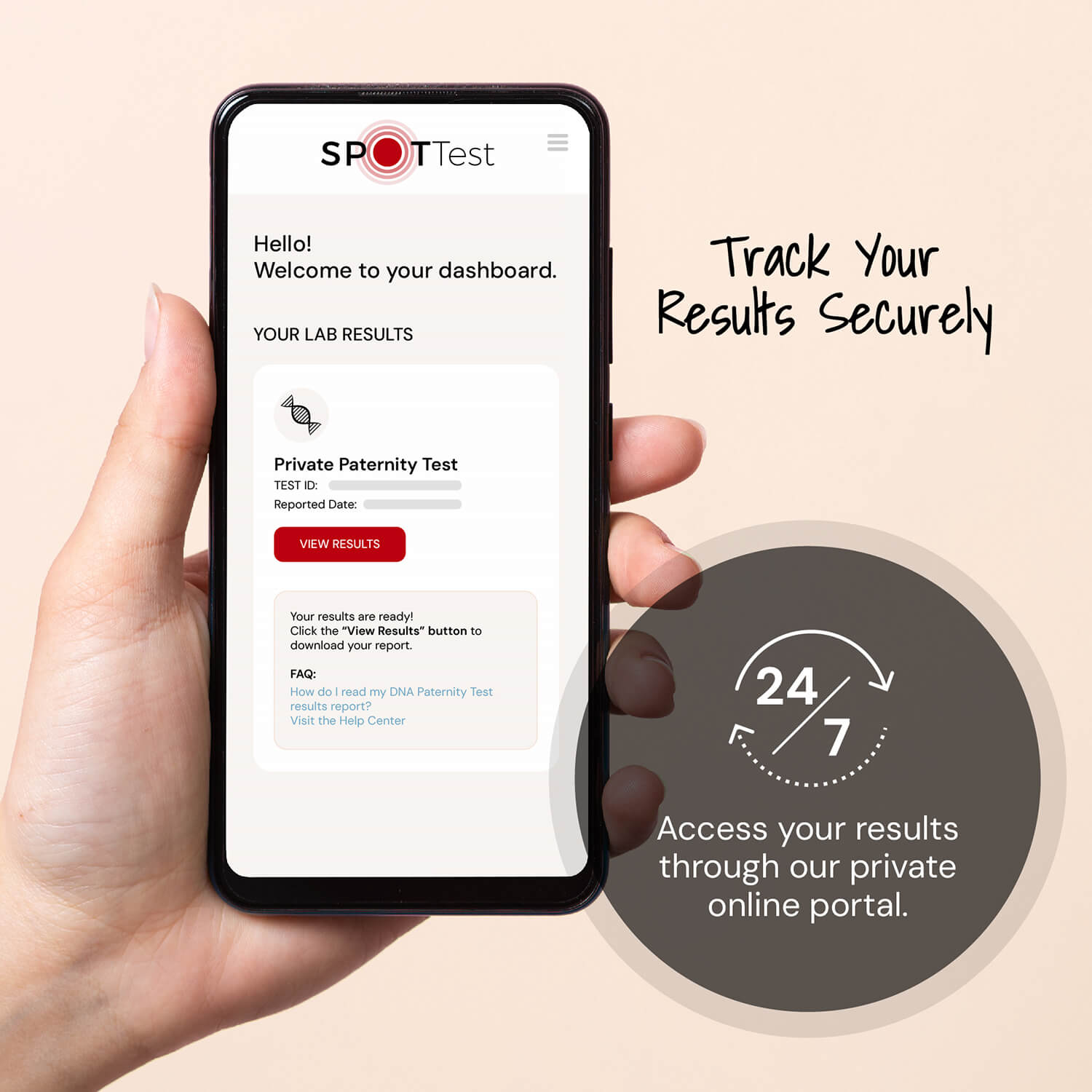
DNA Nutrition Test
Unlock personalized insights into how your body absorbs and uses nutrients.
Measures:
- Determine how well your body absorbs, breaks down, and utilizes vitamins and minerals.
- Assess your risk for potential nutritional deficiencies.
- Optimize your diet for better health.
Collection methods:
Buccal swabs
$249.00
- Discreet shipping
- Accredited lab
- Secure Online Results
- Highest accuracy
- Discreet
- Results in 1-3 business days
About the test
Understanding Your Nutritional Needs
Are you overwhelmed by the thousands of nutrition supplements available, or simply want to ensure you’re getting a balanced intake from food sources?
Your genetic makeup plays a key role in how effectively your body absorbs and utilizes vitamins and minerals. There’s no “one-size-fits-all” supplement or “perfect diet” that works for everyone.
Genetic Profile
What gets measured?
Many genetic variants influence how well we absorb, activate and use specific vitamins and minerals. An understanding of your genetic variation allows you to customize your nutritional planning.
Vitamin A is important for vision, immune function, skin health, bone growth and reproduction.
• BCO1 – affects activation of vitamin A
Vitamin B6 is needed for carbohydrate metabolism, cognitive development, immune function, skin health and hemoglobin formation.
• NBPF3 – increases clearance of vitamin B6 from the body
Vitamin B12 is necessary for the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and is required for DNA synthesis and the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids.
• FUT2 – reduces absorption of vitamin B12 in the gut
Vitamin C is involved in the production of several critical biological molecules (e.g. collagen and neurotransmitters), immune response, wound healing, absorption of non-heme iron, and as an antioxidant to remove toxic byproducts.
• SLC23A1 – decreases vitamin C absorption and distribution
Vitamin D is required to modulate cell growth, aid in immune functions, decrease inflammation and maintain normal bone growth and remodelling.
• CYP2R1 – reduces activation of vitamin D
• GC – reduces efficiency of vitamin D transport and uptake
Vitamin E promotes the immune system, healthy eyes and skin, as well as a number of other metabolic processes.
• APOA5 – influences vitamin E levels
Folate is essential for proper growth and development, and is important for the conversion of the toxic homocysteine amino acid to methionine.
• MTHFD1 – linked to folate-related disorders
• MTHFR – affects activation of folate
Iron is required to make hemoglobin – an essential protein that transports oxygen around the body.
• TMPRSS6 – influences iron absorption from the diet
• TF – influences iron transport
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for normal, healthy metabolism.
• NOS3 – influences triglyceride levels when omega-3 is low
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is important for vision, immune function, skin health, bone growth and reproduction.
• BCO1 – affects activation of vitamin A
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is needed for carbohydrate metabolism, cognitive development, immune function, skin health and hemoglobin formation.
• NBPF3 – increases clearance of vitamin B6 from the body
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is necessary for the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and is required for DNA synthesis and the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids.
• FUT2 – reduces absorption of vitamin B12 in the gut
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is involved in the production of several critical biological molecules (e.g. collagen and neurotransmitters), immune response, wound healing, absorption of non-heme iron, and as an antioxidant to remove toxic byproducts.
• SLC23A1 – decreases vitamin C absorption and distribution
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is required to modulate cell growth, aid in immune functions, decrease inflammation and maintain normal bone growth and remodelling.
• CYP2R1 – reduces activation of vitamin D
• GC – reduces efficiency of vitamin D transport and uptake
Vitamin E
Vitamin E promotes the immune system, healthy eyes and skin, as well as a number of other metabolic processes.
• APOA5 – influences vitamin E levels
Folate
Folate is essential for proper growth and development, and is important for the conversion of the toxic homocysteine amino acid to methionine.
• MTHFD1 – linked to folate-related disorders
• MTHFR – affects activation of folate
Iron
Iron is required to make hemoglobin – an essential protein that transports oxygen around the body.
• TMPRSS6 – influences iron absorption from the diet
• TF – influences iron transport
Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for normal, healthy metabolism.
• NOS3 – influences triglyceride levels when omega-3 is low
How it works


CHOOSE TEST

COLLECT SAMPLE

GET YOUR RESULTS

You might also like
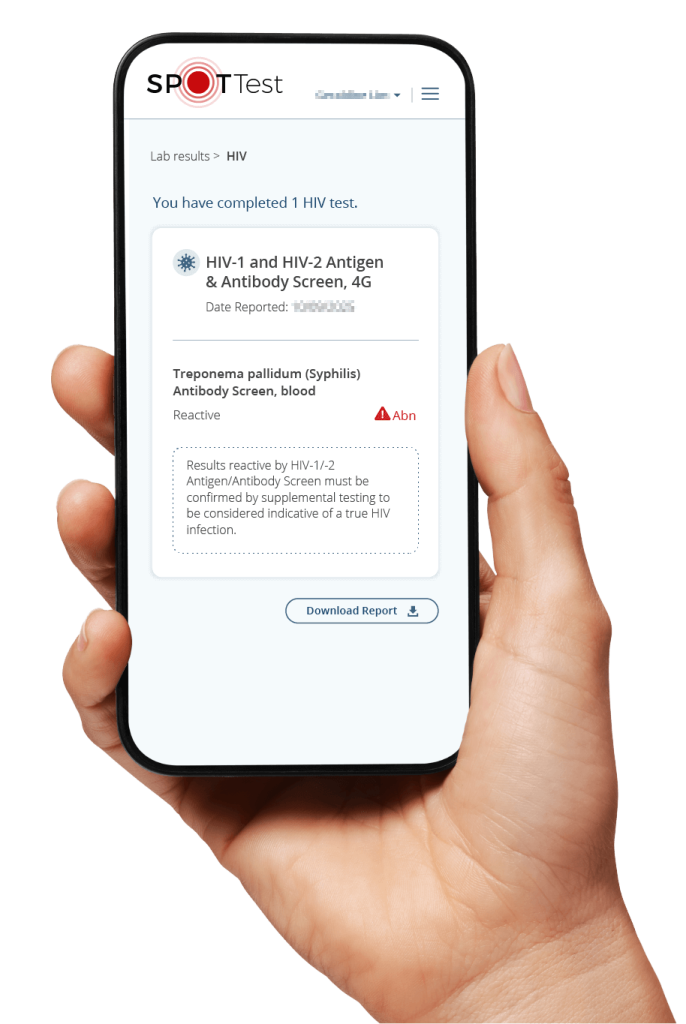
What gets measured?
Many genetic variants influence how well we absorb, activate and use specific vitamins and minerals. An understanding of your genetic variation allows you to customize your nutritional planning.